News
University of Eastern Finland leads programme to revive Karelian
The Karelian language revitalisation project has received funding from the Ministry of Education and Culture of Finland to continue the programme.
New language technology developed for Uralic languages
This year, there has been progress in developing modern software for the Uralic languages. Programmes related to Udmurt and Mari are being developed, in addition to a Uralic-language machine translation engine at the University of Tartu.
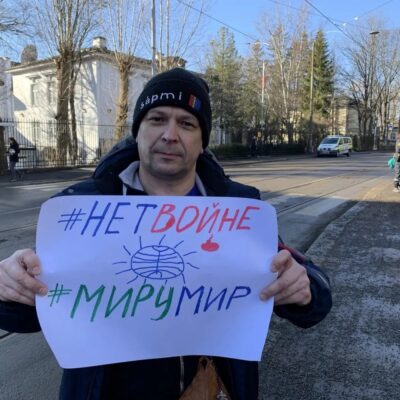
Saami fighting on both sides of front in Ukraine
The Saami community in Russia was divided in half after the war in Ukraine began. Some of the Saami have taken part in protests in support of the Russian attack, Justas Stasevskiy reports on YLE.
Mordvins in Russian Federation celebrated Erzya Language Day
Since 1993, April 16 has been celebrated as the Erzya Language Day. Some years ago, the day was changed in the Russian Federation to the Mordvin Language Day.
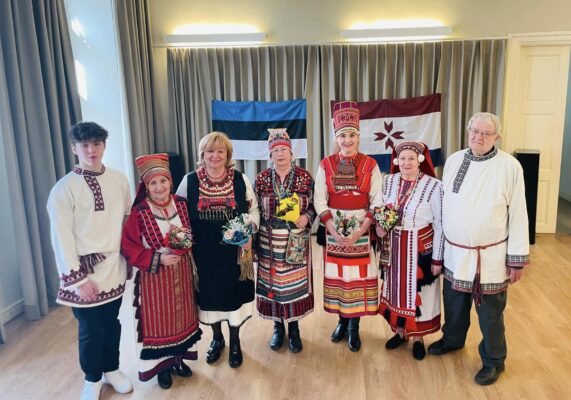
Estonian Mordvins celebrated Erzya Language Day
Mordvins living in Estonia celebrated the Erzya Language Day on April 14. The event was organised by the Estonian Mordvin Culture Society and the Erzya Cultural Association Syatko at the Tallinn Folk High School.
Komi Language and Writing Day officially celebrated in Republic of Komi
The Komi Language and Writing Day is celebrated on the third Sunday of May in the Republic of Komi.
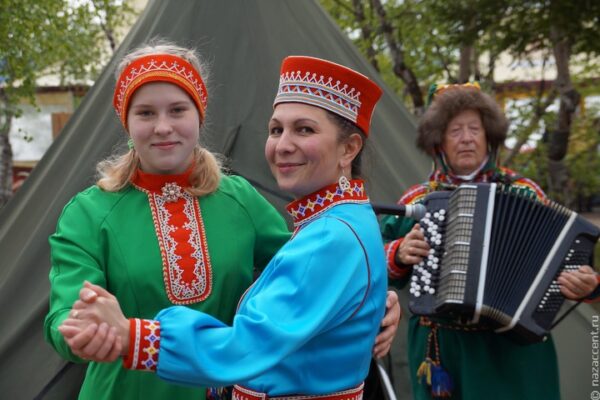
Saami Language Centre opened in Murmansk
The Sami Language Support Centre has been opened at the Institute of Linguistics of the Murmansk Arctic State University. The university is the only institution in Russia that teaches the Sami language in the master's degree.
Finno-Ugrian days return this October
The festival reaches its apex on the third Saturday of October – this year on October 15th – the day that the national flags of Estonia fly in honour of our fellow kindred peoples living all around the world.
Ethnic Science Award 2022: Kindred People's Programme calls for nominations
This year, the competition welcomes the works of researchers who are based outside of the Russian Federation. Applications should be submitted electronically. The deadline for submitting nominations is 31 August 2022.
The Nordic Pavilion Becomes the First Sámi Pavilion
For the first time, only Sámi artists will be presented in a national pavilion at the Venice Biennale, and for the first time, the Sámi will be recognised as a nation in a pavilion that bears their name.
Fenno-Ugria condemns the aggression by the Russian Federation in Ukraine
We do not consider cooperation possible with Finno-Ugric peoples’ organisations and individuals that support military action against Ukraine by the Russian Federation, until they stop supporting the activities against humanity by the leadership of their country.
Finnish town Kuhmo selected as Finno-Ugric Capital of Culture 2023
This marks the first time that the Finno-Ugric Capital of Culture will be located in Finland. Kuhmo expects the title to boost cultural tourism in the region and to support the preservation and revitalization of languages and cultural heritage across the wider Finno-Ugric world.