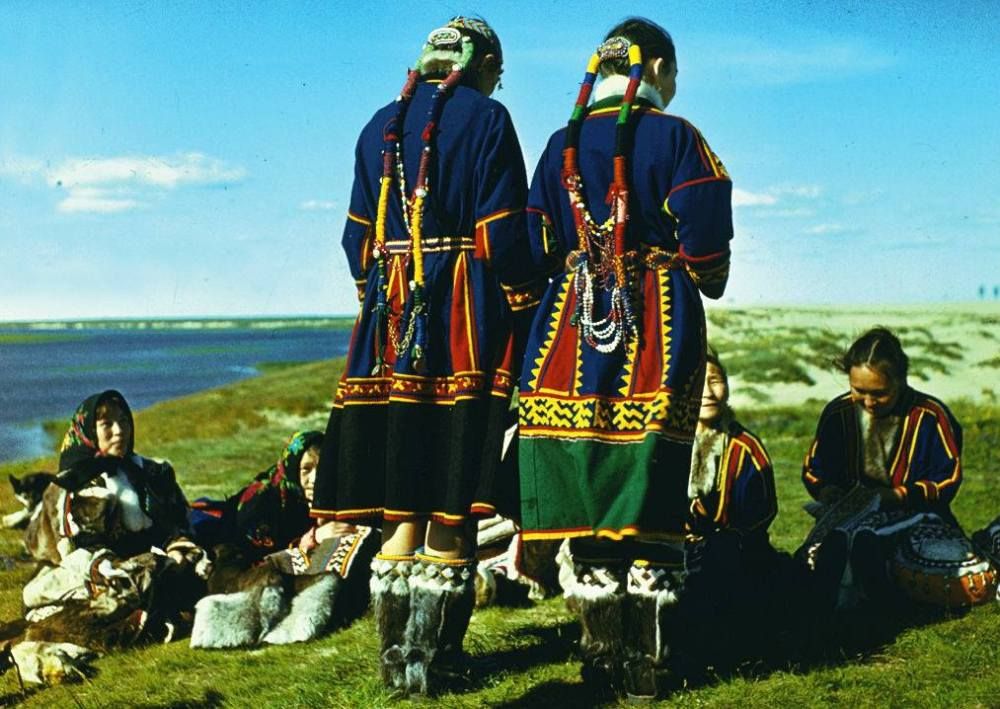

Samoyedic peoples
Samoyed languages are languages of the Uralic language family.
Samoyedic peoples include Nenets, Enets, Nganasans and Selkups. Samoyedic languages are languages of the Uralic language family which are spoken by Samoyedic peoples inhabiting the northern parts of Eurasia in Russia.
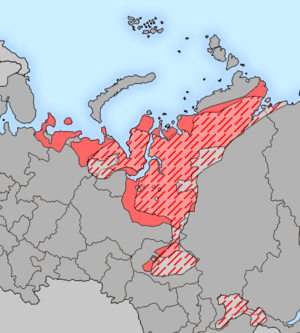
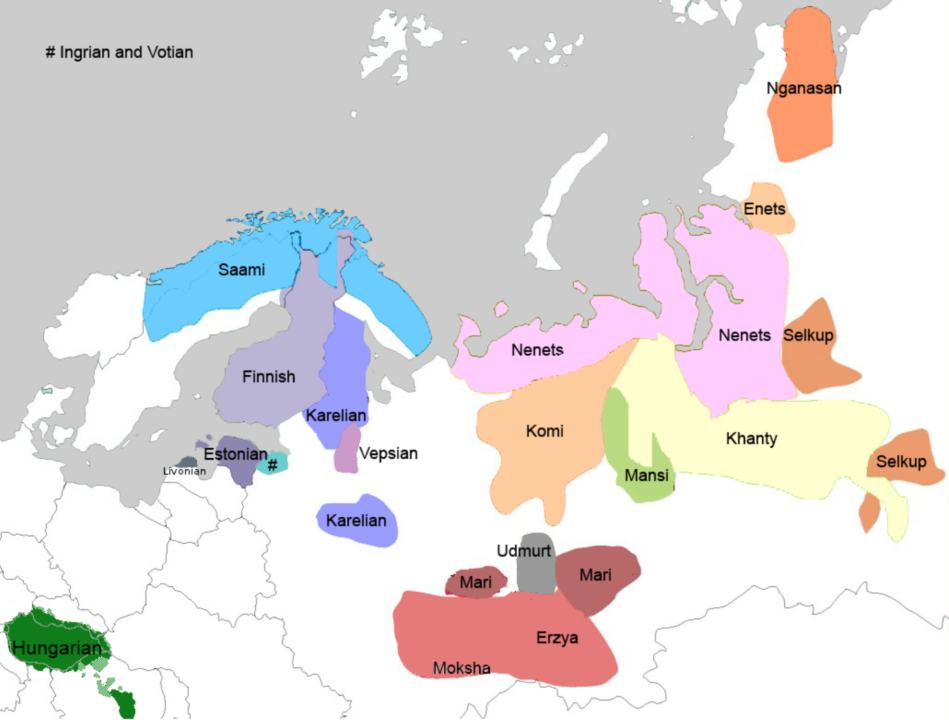
Samoyedic languages include
- Nenets (31,311 speakers) with two main dialects which are often considered separate languages:
- Tundra Nenets – an endangered language in the Nenets and Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Regions and in the Taimyr region of Krasnoyarsk Krai
- Forest Nenets – a seriously endangered language in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Region
- Enets (119 speakers) – a disappearing language in North Siberia’s Taimyr Autonomous Region at the Yenisei River, with two main dialects: Forest Enets and Tundra Enets, which are usually considered separate languages.
- Nganasan (505 speakers) – a seriously endangered language in Siberia’s Taimyr peninsula.
- Selkup (1,641 speakers) – a seriously endangered language in Western Siberia between Ob and Yenisei Rivers.
- Kamass – an extinct language (last speaker Klavdiya Plotnikova died in 1989)
- Mator – a Samoyed language that became extinct at the beginning of the 19th century. Its dialects were Taigi and Karagassian.
- Koibal – a Samoyed language that became extinct at the beginning of the 19th century. May have been a dialect of Kamass.


